Deployment Steps¶
The complete steps of the deployment process available as Ansible playbooks in docs/examples.
Prepare the production image¶
restknot-api needs a config.yml file to run. You can supply the file
outside the image using docker volume. Or build the new image containing your
production version of config.yml.
# Dockerfile
FROM biznetgio/restknot-api:latest
COPY config.yml /restknotapi
Prepare the required files¶
Before running the playbooks you have to create a folder named configs with
the required files. Namely the docker-compose.yml for both restknot-agent
and restknot-api, schema.sql, and the knot.conf for both master and
slave files. All of them available in the example directory.
Modify the value of those files to match your production environment.
config.ymlholds application configurations, mainly a list of Knot servers and a list of Kafka brokers.knot.confserves as a configuration for the Knot DNS server.schema.sqlused to define the DB schema.- (Optional)
kowl.ymlfile for Kafka viewer.
The most important thing you have to pay attention to is RESTKNOT_AGENT_TYPE,
it will not work if you set it to slave but the app runs on the master node.
Get the keys of your machines¶
- Put the key of your machine in one directory .e.g ~/ssh-keys/
- Point the ansible to those keys .e.g
all:
vars:
ansible_private_key_file: "~/ssh-keys/vm-key.pem"
Play the Playbook¶
$ # initial setup for machine
$ ansible-playbook initial-setups.yml --forks=10 -v
$ # prepare the machine for restknot-api
$ ansible-playbook setup-api.yml --forks=10 -v
$ # test one the playbook to of the nodes
$ ansible-playbook setup-agent.yml --forks=10 --extra-vars="target_host=10.0.0.3" -v
$ # prepare the machine for restknot-agent
$ ansible-playbook setup-agent.yml --forks=10 -v
Basic Deployment Architecture¶
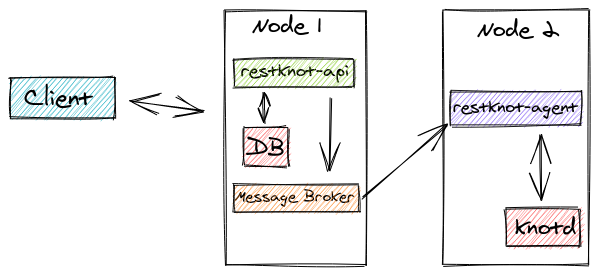
A basic deployment architecture.
There are many possible forms in the deployment. But the most basic is using a
two-node. The first node is going to host restknot-api,
database, and message broker. The second node is hosting Knot DNS server
(knotd) and restknot-agent.
The three components in the first node can be run using a docker container. You
can use the api/docker-compose.example.yml as a starting point. For the
second node, it’s advised that you install the knot server locally, then you
can use agent/docker-compose.example.yml for the agent.